Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Guide to the Chronic Autoimmune Disease
by twib
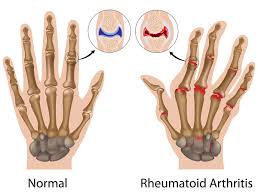
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Understanding the Chronic Autoimmune Disease
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and stiffness. This condition occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues, particularly the synovium – the lining of the joints.
RA can lead to joint damage and deformity if left untreated. Common symptoms include joint swelling, tenderness, warmth, and morning stiffness lasting for more than an hour. The disease can also affect other parts of the body, such as the skin, eyes, lungs, and heart.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of rheumatoid arthritis is unknown. However, certain factors may contribute to its development:
- Genetics: Individuals with a family history of RA are at a higher risk.
- Environmental Triggers: Smoking and exposure to certain infections may increase susceptibility.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop RA than men.
- Age: Although RA can occur at any age, it most commonly begins between ages 30 and 60.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis, early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression. Treatment strategies may include:
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biologic agents are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises can improve joint function and flexibility.
- Surgery: In severe cases, joint replacement surgery may be necessary to restore mobility.
Lifestyle Tips
In addition to medical interventions, lifestyle modifications can help individuals with RA manage their condition effectively:
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce stress on joints.
- Engage in regular exercise to strengthen muscles and improve joint flexibility.
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis: Key Questions and Answers
- What is rheumatoid arthritis?
- What are the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis?
- Is there a cure for rheumatoid arthritis?
- How is rheumatoid arthritis diagnosed?
- What are the treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis?
- Are there lifestyle changes that can help manage rheumatoid arthritis?
What is rheumatoid arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily targets the joints, leading to inflammation, pain, and stiffness. This condition occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues, particularly the synovium – the lining of the joints. Rheumatoid arthritis can cause joint damage and deformity if left untreated, affecting not only mobility but also overall quality of life. Common symptoms include joint swelling, tenderness, warmth, and morning stiffness lasting for more than an hour. Understanding rheumatoid arthritis is crucial in seeking early diagnosis and appropriate treatment to manage its impact on daily life.
What are the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis is characterized by a range of symptoms that primarily affect the joints. Common signs of rheumatoid arthritis include joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and tenderness. Individuals with this condition may experience morning stiffness that lasts for more than an hour, making it challenging to move the affected joints. Inflammation in the joints can lead to reduced range of motion and deformity over time. Other symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis may involve fatigue, fever, weight loss, and overall feelings of malaise. It is essential to recognize these symptoms early on and seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and management.
Is there a cure for rheumatoid arthritis?
In response to the frequently asked question, “Is there a cure for rheumatoid arthritis?” it is important to note that currently, there is no known cure for rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disease that requires long-term management to control symptoms and prevent joint damage. While treatment options such as medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications can help improve quality of life for individuals with RA, it is essential to work closely with healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan that best suits the individual’s needs. Early diagnosis and proactive management are key in effectively managing rheumatoid arthritis.
How is rheumatoid arthritis diagnosed?
Diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Healthcare providers may inquire about symptoms such as joint pain, stiffness, and swelling, along with family history of autoimmune conditions. A thorough physical exam can reveal signs of inflammation in the joints. Blood tests measuring inflammatory markers like C-reactive protein (CRP) and rheumatoid factor (RF) are often conducted to support the diagnosis. Additionally, imaging tests such as X-rays and ultrasound may be used to assess joint damage. A definitive diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis is made based on a comprehensive evaluation of these factors by a healthcare professional experienced in managing autoimmune disorders.
What are the treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis?
When it comes to managing rheumatoid arthritis, there are various treatment options available to help alleviate symptoms and slow down disease progression. Common approaches include the use of medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biologic agents to reduce inflammation and pain. Physical therapy is often recommended to improve joint function and flexibility. In some cases, surgery, such as joint replacement, may be necessary for severe joint damage. It’s essential for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis to work closely with healthcare professionals to determine the most suitable treatment plan tailored to their specific needs and condition.
Are there lifestyle changes that can help manage rheumatoid arthritis?
Many individuals wonder if lifestyle changes can aid in managing rheumatoid arthritis. The answer is yes – adopting certain lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in easing symptoms and improving quality of life for those with RA. Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise tailored to individual needs, and following a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods are key components to consider. Additionally, managing stress levels, getting adequate rest, and seeking support from healthcare professionals can all contribute to better management of rheumatoid arthritis.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Understanding the Chronic Autoimmune Disease Rheumatoid Arthritis: Understanding the Chronic Autoimmune Disease Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and stiffness. This condition occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues, particularly the synovium – the lining of the joints. RA…
Latest articles
- The Legendary Legacy of the LA Angels: A Beacon in Baseball History
- Breaking Lakers News: Latest Updates and Developments from the Court
- Unleashing the Power of Hockey: A Thrilling Journey on the Ice
- Harry Souttar: Australia’s Defensive Dynamo Making Waves in Football
- Unveiling the Enigma: The Intriguing Harry Brook
Latest comments
Archive
- March 2026
- February 2026
- January 2026
- December 2025
- November 2025
- October 2025
- September 2025
- August 2025
- July 2025
- June 2025
- May 2025
- April 2025
- March 2025
- February 2025
- January 2025
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
