Navigating Life with Celiac Disease: Understanding the Challenges and Triumphs
by twib
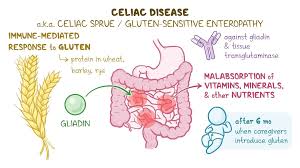
The Lowdown on Celiac Disease
Celiac disease is a serious autoimmune disorder that affects individuals who are genetically predisposed to gluten intolerance. When people with celiac disease consume gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye, their immune system responds by attacking the small intestine. This immune reaction damages the lining of the small intestine, leading to various symptoms and complications.
Symptoms
The symptoms of celiac disease can vary widely among individuals. Common symptoms include gastrointestinal issues such as bloating, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, and nausea. Some people may also experience fatigue, joint pain, skin rashes, and unexplained weight loss. In children, celiac disease can lead to stunted growth and developmental delays.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing celiac disease involves a combination of blood tests and intestinal biopsies. Blood tests can detect specific antibodies that are elevated in individuals with celiac disease. If blood tests suggest celiac disease, a gastroenterologist may perform an endoscopy to take biopsies of the small intestine to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment
The only effective treatment for celiac disease is a strict gluten-free diet. By eliminating gluten from their diet, individuals with celiac disease can allow their small intestine to heal and prevent further damage. It’s essential for those with celiac disease to be vigilant about reading food labels and avoiding cross-contamination to maintain their health.
Complications
If left untreated, celiac disease can lead to serious complications such as malnutrition, osteoporosis, infertility, neurological disorders, and an increased risk of certain cancers. It’s crucial for individuals with celiac disease to adhere strictly to a gluten-free diet to prevent these long-term consequences.
Conclusion
Celiac disease is a chronic condition that requires lifelong management through dietary modifications. By raising awareness about this condition and promoting early diagnosis and treatment, we can help improve the quality of life for those living with celiac disease. If you suspect you may have celiac disease or know someone who does, consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance.
Five Essential Tips for Managing Coeliac Disease Effectively
- Avoid gluten-containing foods such as wheat, barley, and rye.
- Read food labels carefully to identify hidden sources of gluten.
- Choose naturally gluten-free grains like rice, quinoa, and corn.
- Be cautious when dining out and ask about gluten-free options or food preparation methods.
- Consult a healthcare professional or dietitian for personalized advice on managing celiac disease.
Avoid gluten-containing foods such as wheat, barley, and rye.
To manage celiac disease effectively, it is crucial to steer clear of gluten-containing foods like wheat, barley, and rye. These grains contain gluten, a protein that triggers an immune response in individuals with celiac disease, leading to intestinal damage and various symptoms. By eliminating these sources of gluten from your diet, you can help alleviate symptoms, promote intestinal healing, and prevent further complications associated with this autoimmune disorder. Embracing a gluten-free lifestyle is key to maintaining good health and well-being for those living with celiac disease.
Read food labels carefully to identify hidden sources of gluten.
When managing celiac disease, it’s crucial to read food labels diligently to uncover hidden sources of gluten. Many processed foods contain gluten as an additive or in the form of ingredients like modified food starch or malt flavoring. By paying close attention to labels and being aware of potential sources of gluten, individuals with celiac disease can make informed choices and safeguard their health by avoiding products that could trigger adverse reactions.
Choose naturally gluten-free grains like rice, quinoa, and corn.
When managing celiac disease, opting for naturally gluten-free grains such as rice, quinoa, and corn can be a smart dietary choice. These grains are safe for individuals with celiac disease and provide essential nutrients while avoiding gluten-related complications. Incorporating a variety of naturally gluten-free grains into your meals can help diversify your diet and ensure you’re meeting your nutritional needs without sacrificing taste or texture. By making informed choices like selecting rice, quinoa, and corn, individuals with celiac disease can enjoy a balanced and satisfying diet that supports their overall health and well-being.
Be cautious when dining out and ask about gluten-free options or food preparation methods.
When dining out, individuals with celiac disease should exercise caution and inquire about gluten-free options or the food preparation methods. It’s essential to communicate your dietary needs clearly to restaurant staff to ensure that your meal is safe to consume. By being proactive and asking questions about gluten-free choices or how dishes are prepared, you can reduce the risk of accidental gluten exposure and enjoy a worry-free dining experience. Remember, advocating for your health is key when managing celiac disease in social settings.
Consult a healthcare professional or dietitian for personalized advice on managing celiac disease.
It is highly recommended to seek guidance from a healthcare professional or dietitian for personalized advice on managing celiac disease. These experts can provide tailored recommendations based on individual needs and health status, helping individuals navigate the complexities of a gluten-free lifestyle effectively. By consulting with professionals experienced in celiac disease management, individuals can receive the support and information necessary to maintain optimal health and well-being while adhering to a gluten-free diet.
The Lowdown on Celiac Disease Celiac disease is a serious autoimmune disorder that affects individuals who are genetically predisposed to gluten intolerance. When people with celiac disease consume gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye, their immune system responds by attacking the small intestine. This immune reaction damages the lining of the small…
