Combatting Influenza: Strategies for Flu Prevention and Protection
by twib
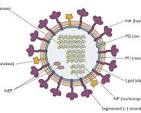
The Impact of Influenza: Understanding the Flu Virus
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is a highly contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses. Each year, millions of people worldwide are affected by this infectious disease, leading to significant morbidity and mortality.
The flu virus primarily spreads through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Symptoms of influenza can vary from mild to severe and may include fever, cough, sore throat, body aches, fatigue, and headache. In some cases, complications such as pneumonia can arise, especially in vulnerable populations like the elderly, young children, pregnant women, and individuals with underlying health conditions.
Prevention is key in combating the spread of influenza. Vaccination remains the most effective way to protect against the flu and reduce its impact on public health. Annual flu shots are recommended to provide immunity against prevalent strains of the virus.
Additionally, practicing good hygiene habits such as frequent handwashing, covering coughs and sneezes, and staying home when sick can help prevent the transmission of the flu virus. Early detection and prompt treatment with antiviral medications can also lessen the severity and duration of symptoms.
During flu season, healthcare systems often experience increased demand for services due to a surge in influenza-related illnesses. Hospitals may implement measures to manage patient influx and prevent further spread of the virus within healthcare settings.
Public awareness campaigns play a vital role in educating individuals about influenza prevention strategies and promoting vaccination uptake. By staying informed and taking proactive steps to protect themselves and others from the flu, people can contribute to reducing the burden of this infectious disease on society.
Eight Key Benefits of Addressing Influenza: From Vaccination to Public Health Advancements
- Annual flu vaccination helps build immunity against prevalent strains.
- Increased awareness of hygiene practices to prevent flu transmission.
- Research on influenza contributes to advancements in virology and public health.
- Early detection of flu symptoms allows for timely treatment and management.
- Healthcare systems develop protocols for handling seasonal influenza outbreaks.
- Flu prevention measures can reduce absenteeism and improve productivity in workplaces.
- Public health campaigns raise awareness about the importance of flu vaccination.
- Understanding influenza epidemiology aids in predicting and preparing for future outbreaks.
Understanding the Challenges of Influenza: Contagion, Complications, and Community Impact
- Highly contagious respiratory illness
- Symptoms can range from mild to severe
- Risk of complications such as pneumonia
- Increased healthcare burden during flu season
- Potential for rapid spread within communities
- Impact on vulnerable populations like the elderly and young children
Annual flu vaccination helps build immunity against prevalent strains.
Annual flu vaccination plays a crucial role in building immunity against prevalent strains of influenza. By receiving a flu shot each year, individuals can enhance their immune response to specific strains of the virus, reducing the likelihood of contracting the flu and its potential complications. This proactive approach not only protects the vaccinated individual but also contributes to community immunity, helping to curb the spread of influenza and safeguarding vulnerable populations who may be at higher risk of severe illness.
Increased awareness of hygiene practices to prevent flu transmission.
The presence of influenza has led to a positive outcome of heightened awareness regarding the importance of hygiene practices in preventing the transmission of the flu virus. Individuals are now more conscious of maintaining good hygiene habits such as regular handwashing, covering coughs and sneezes, and staying home when feeling unwell. This increased focus on cleanliness not only helps in reducing the spread of influenza but also contributes to overall public health by minimizing the risk of other infectious diseases.
Research on influenza contributes to advancements in virology and public health.
Studying influenza plays a crucial role in driving progress in virology and public health initiatives. Research focused on understanding the flu virus not only leads to insights into its transmission and evolution but also paves the way for developing effective prevention strategies such as vaccines. By delving into the intricacies of influenza, scientists can enhance their knowledge of viral diseases in general, ultimately benefiting public health efforts worldwide. The findings from influenza research serve as building blocks for broader scientific advancements, shaping our ability to combat infectious diseases and safeguard communities against future viral threats.
Early detection of flu symptoms allows for timely treatment and management.
Timely detection of flu symptoms is a crucial advantage when dealing with influenza. By recognizing the early signs of the flu, individuals can seek prompt medical attention and receive appropriate treatment to manage the illness effectively. Early intervention not only helps alleviate symptoms but also reduces the risk of complications and speeds up the recovery process. Being vigilant about flu symptoms enables individuals to take proactive steps to protect their health and prevent the spread of the virus to others, ultimately contributing to better outcomes for both individuals and communities as a whole.
Healthcare systems develop protocols for handling seasonal influenza outbreaks.
During seasonal influenza outbreaks, one significant advantage is that healthcare systems develop protocols to effectively manage the increased demand for medical services. These protocols help healthcare facilities streamline patient care, allocate resources efficiently, and implement infection control measures to prevent further spread of the flu virus within healthcare settings. By having established procedures in place, healthcare providers can respond promptly to the surge in influenza cases, ensuring that patients receive timely treatment and reducing strain on the overall healthcare system.
Flu prevention measures can reduce absenteeism and improve productivity in workplaces.
Implementing flu prevention measures in workplaces can have a positive impact on reducing absenteeism and enhancing productivity. By promoting practices such as vaccination, proper hand hygiene, and staying home when sick, employers can create a healthier work environment that minimizes the spread of influenza among employees. When staff members are healthy and protected against the flu virus, they are less likely to call in sick, leading to improved attendance rates and overall productivity levels within the workplace. Investing in flu prevention not only benefits individual employees by safeguarding their health but also contributes to the efficiency and success of businesses by maintaining a workforce that is present and engaged.
Public health campaigns raise awareness about the importance of flu vaccination.
Public health campaigns play a crucial role in raising awareness about the significance of flu vaccination. By educating the public about the benefits of getting vaccinated against influenza, these campaigns help individuals make informed decisions to protect themselves and others from the virus. Encouraging vaccination uptake through targeted messaging and outreach efforts can contribute to reducing the spread of flu, minimizing illness severity, and ultimately safeguarding community health during flu season.
Understanding influenza epidemiology aids in predicting and preparing for future outbreaks.
Understanding influenza epidemiology is crucial as it enables healthcare professionals and policymakers to anticipate and plan for future outbreaks effectively. By analysing trends in flu transmission, identifying high-risk populations, and monitoring the evolution of influenza viruses, experts can develop targeted prevention strategies and allocate resources efficiently. This proactive approach not only helps in mitigating the impact of potential outbreaks but also contributes to better preparedness in managing public health crises related to influenza. By staying abreast of influenza epidemiology, we can enhance our ability to respond swiftly and effectively to emerging threats posed by this infectious disease.
Highly contagious respiratory illness
Influenza, as a highly contagious respiratory illness, poses a significant public health challenge due to its rapid spread within communities. The ease with which the flu virus can be transmitted through respiratory droplets makes containment efforts challenging, especially during peak flu seasons. This contagious nature of influenza not only increases the risk of widespread outbreaks but also places vulnerable individuals, such as the elderly and those with weakened immune systems, at a higher likelihood of contracting the virus. Effective preventive measures, including vaccination and adherence to proper hygiene practices, are crucial in mitigating the impact of this airborne disease and reducing its transmission rates.
Symptoms can range from mild to severe
Influenza, or the flu, presents a significant challenge due to the wide spectrum of symptoms it can cause, ranging from mild to severe. This variability in symptom severity makes it difficult for individuals to predict how the virus will affect them, leading to uncertainty and potential complications. While some people may experience only mild discomfort such as a runny nose and slight fever, others could develop severe respiratory issues and complications that require medical intervention. This unpredictability underscores the importance of taking preventive measures such as vaccination and practicing good hygiene to reduce the risk of contracting and spreading the flu virus.
Risk of complications such as pneumonia
Influenza poses a significant con in the form of an increased risk of complications, most notably pneumonia. When individuals contract the flu virus, especially those in high-risk groups such as the elderly or individuals with underlying health conditions, they are more susceptible to developing secondary infections like pneumonia. Pneumonia can lead to severe respiratory issues and further exacerbate the already taxing symptoms of influenza, making it crucial for individuals to take preventive measures such as vaccination and prompt medical attention to reduce the likelihood of such complications.
Increased healthcare burden during flu season
During flu season, one significant con of influenza is the increased healthcare burden it places on medical facilities and professionals. The surge in influenza cases leads to higher patient volumes seeking treatment for flu-related symptoms, putting strain on healthcare resources and personnel. Hospitals may face challenges in managing the influx of patients, leading to longer wait times, overcrowded emergency departments, and potential shortages of medical supplies. Healthcare workers work tirelessly to provide care for those affected by the flu while also addressing other medical needs, highlighting the importance of preparedness and resource allocation to meet the heightened demand during this period.
Potential for rapid spread within communities
Influenza poses a significant con due to its potential for rapid spread within communities. The highly contagious nature of the flu virus means that it can quickly proliferate among populations, leading to widespread outbreaks and increased transmission rates. This rapid spread not only challenges public health authorities in containing the virus but also heightens the risk of vulnerable individuals being exposed to the illness. Efforts to curb the rapid dissemination of influenza require coordinated strategies such as vaccination campaigns, public health interventions, and community awareness initiatives to mitigate its impact on community health and well-being.
Impact on vulnerable populations like the elderly and young children
Influenza poses a significant con by disproportionately impacting vulnerable populations such as the elderly and young children. These demographic groups are particularly susceptible to severe complications from the flu due to their weaker immune systems and underlying health conditions. For the elderly, influenza can lead to serious respiratory problems and exacerbate existing health issues, increasing the risk of hospitalization and mortality. Similarly, young children may experience more severe symptoms and complications from the flu, requiring close monitoring and medical intervention. Protecting these vulnerable populations through vaccination and preventive measures is crucial in reducing the burden of influenza-related illnesses and safeguarding public health.
The Impact of Influenza: Understanding the Flu Virus The Impact of Influenza: Understanding the Flu Virus Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is a highly contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses. Each year, millions of people worldwide are affected by this infectious disease, leading to significant morbidity and mortality. The flu virus primarily spreads…
Latest articles
- Balancing Act: Nurturing Your Lifestyle’s Essence for Well-being
- Unveiling the Legacy of Micah Richards: A Footballing Icon
- Unveiling the Excitement: The Mexican Open Tennis Tournament in Acapulco
- Stay In the Loop: Man Utd News Now Uncovered!
- Exploring the Depths: The Fascinating World of Marine Biology
Latest comments
Archive
- March 2026
- February 2026
- January 2026
- December 2025
- November 2025
- October 2025
- September 2025
- August 2025
- July 2025
- June 2025
- May 2025
- April 2025
- March 2025
- February 2025
- January 2025
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
