Understanding Gout: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment in Australia
by twib
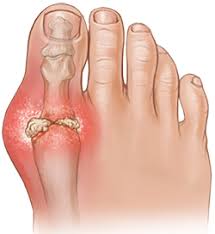
Gout: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis that develops in people with high levels of uric acid in their blood. This condition can cause sudden and severe pain, swelling, and redness in joints, most commonly affecting the big toe.
Causes of Gout
Uric acid is a waste product produced by the body during the breakdown of purines found in certain foods and beverages. When uric acid levels become too high, it can form crystals in the joints, leading to gout attacks.
Symptoms of Gout
The most common symptom of gout is intense joint pain that typically starts in the middle of the night. Other symptoms include swelling, redness, warmth, and stiffness in the affected joint. Gout attacks can last for a few days to weeks.
Treatment for Gout
Treatment for gout aims to relieve pain during attacks and prevent future flare-ups. This may involve medications to reduce inflammation and lower uric acid levels in the blood. Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet low in purines and staying hydrated can also help manage gout.
Preventing Gout
Preventing gout involves making dietary changes to avoid foods high in purines such as red meat, organ meats, and certain types of seafood. Limiting alcohol consumption and staying hydrated are also essential steps to reduce the risk of gout attacks.
In conclusion, gout is a painful condition caused by high levels of uric acid in the blood. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can better manage this form of arthritis and improve their quality of life.
Effective Management and Prevention Strategies for Gout: Key Benefits Explored
- Gout can be effectively managed with medication and lifestyle changes.
- Symptoms of gout, such as joint pain and swelling, can be controlled with proper treatment.
- Treatment for gout can help prevent future flare-ups and complications.
- Making dietary modifications to reduce purine intake can benefit overall health in addition to managing gout.
- Regular monitoring of uric acid levels can help individuals stay proactive in managing their condition.
- By understanding the causes and triggers of gout, individuals can take steps to prevent its onset or recurrence.
Challenges of Managing Gout: Pain, Joint Damage, Dietary Changes, and Medication Concerns
- Gout can cause severe pain and discomfort during flare-ups.
- Untreated gout can lead to joint damage and deformities over time.
- People with gout may need to make significant dietary changes to manage the condition.
- Certain medications used to treat gout may have side effects or interactions with other drugs.
Gout can be effectively managed with medication and lifestyle changes.
Gout, a form of inflammatory arthritis, offers a silver lining in the fact that it can be effectively managed through a combination of medication and lifestyle adjustments. By adhering to prescribed medications to reduce inflammation and lower uric acid levels in the blood, coupled with adopting healthy habits like maintaining a diet low in purines and staying well-hydrated, individuals can take proactive steps in controlling gout flare-ups and improving their overall quality of life.
Symptoms of gout, such as joint pain and swelling, can be controlled with proper treatment.
Symptoms of gout, including debilitating joint pain and swelling, can be effectively managed with appropriate treatment. By seeking timely medical intervention and adhering to prescribed therapies, individuals experiencing gout can alleviate discomfort and improve their overall quality of life. Proper management of gout symptoms not only helps in reducing pain and inflammation but also minimizes the risk of recurrent flare-ups, allowing individuals to lead a more active and comfortable lifestyle.
Treatment for gout can help prevent future flare-ups and complications.
Treatment for gout plays a crucial role in not only alleviating the pain and discomfort associated with gout attacks but also in preventing future flare-ups and potential complications. By effectively managing uric acid levels through medication, dietary changes, and lifestyle adjustments, individuals with gout can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of attacks, ultimately improving their overall quality of life and reducing the risk of long-term joint damage.
Making dietary modifications to reduce purine intake can benefit overall health in addition to managing gout.
Making dietary modifications to reduce purine intake not only helps in managing gout but also offers broader health benefits. By opting for a diet low in purine-rich foods such as red meat and certain seafood, individuals can improve their overall well-being. This approach promotes a healthier lifestyle by encouraging the consumption of nutrient-rich foods that support heart health, weight management, and overall vitality. Therefore, by addressing gout through dietary changes, individuals can enhance their overall health outcomes and well-being in the long run.
Regular monitoring of uric acid levels can help individuals stay proactive in managing their condition.
Regular monitoring of uric acid levels can be a valuable pro in managing gout as it allows individuals to stay proactive in understanding their condition. By keeping track of uric acid levels through routine tests, individuals can identify any fluctuations early on and work with healthcare professionals to make necessary adjustments to their treatment plan. This proactive approach not only helps in preventing gout attacks but also promotes better overall management of the condition, leading to improved quality of life for those affected by gout.
By understanding the causes and triggers of gout, individuals can take steps to prevent its onset or recurrence.
By comprehending the causes and triggers of gout, individuals can proactively take measures to prevent its initial occurrence or recurrence. This awareness empowers individuals to make informed lifestyle choices, such as adopting a diet low in purine-rich foods and maintaining proper hydration levels, which can significantly reduce the risk of experiencing painful gout attacks. Education about the factors contributing to gout not only aids in prevention but also encourages a proactive approach towards managing one’s health and well-being effectively.
Gout can cause severe pain and discomfort during flare-ups.
During gout flare-ups, individuals may experience excruciating pain and discomfort in the affected joints, most commonly the big toe. The severity of the pain can be debilitating, making it challenging to perform daily activities and adversely impacting one’s quality of life. Managing these sudden bouts of intense pain is crucial in effectively dealing with gout and its associated symptoms.
Untreated gout can lead to joint damage and deformities over time.
Untreated gout poses a significant risk of causing joint damage and deformities as time progresses. The accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints can lead to chronic inflammation, eventually resulting in structural changes that affect joint function and appearance. It is crucial to address gout promptly through proper medical intervention and lifestyle modifications to prevent long-term complications that may impact one’s mobility and quality of life.
People with gout may need to make significant dietary changes to manage the condition.
People diagnosed with gout often face the challenge of making substantial dietary adjustments to effectively manage the condition. This may involve reducing the intake of foods high in purines, such as red meat, organ meats, and certain seafood, which can trigger gout attacks. Additionally, limiting alcohol consumption and increasing water intake are crucial steps in maintaining lower uric acid levels and preventing flare-ups. Embracing a healthier diet regimen can be a key aspect of managing gout and improving overall well-being for individuals dealing with this arthritic condition.
Certain medications used to treat gout may have side effects or interactions with other drugs.
Certain medications used to treat gout, while effective in managing the symptoms of the condition, can also present potential drawbacks. Some of these medications may come with side effects that range from mild discomfort to more severe complications. Additionally, there is a risk of interactions with other drugs that a person may be taking for different health issues. It is crucial for individuals undergoing gout treatment to consult with their healthcare provider to ensure that the prescribed medications are suitable for their specific situation and do not pose any adverse effects when combined with other medications.
Gout: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Gout: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis that develops in people with high levels of uric acid in their blood. This condition can cause sudden and severe pain, swelling, and redness in joints, most commonly affecting the big toe. Causes of Gout Uric acid is…
Latest articles
- Stay In the Loop: Man Utd News Now Uncovered!
- Exploring the Depths: The Fascinating World of Marine Biology
- Decoding LDL Cholesterol: Navigating the Path to Heart Health
- The Legendary Legacy of the LA Angels: A Beacon in Baseball History
- Breaking Lakers News: Latest Updates and Developments from the Court
Latest comments
Archive
- March 2026
- February 2026
- January 2026
- December 2025
- November 2025
- October 2025
- September 2025
- August 2025
- July 2025
- June 2025
- May 2025
- April 2025
- March 2025
- February 2025
- January 2025
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
