Understanding the Impact of Fatty Liver Disease on Health
by twib
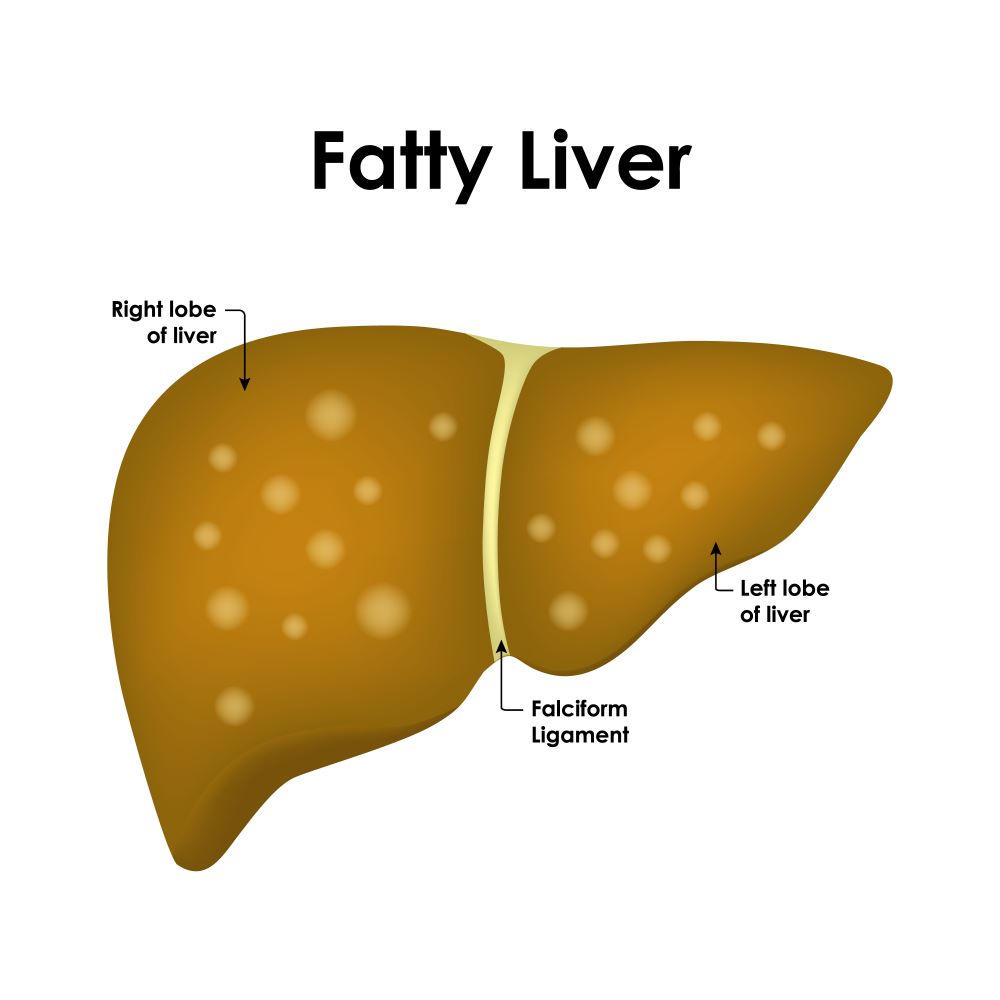
The Silent Threat: Understanding Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition that occurs when fat accumulates in the liver. While it’s normal to have some fat in the liver, excessive fat can lead to serious health issues. This condition often goes unnoticed as it may not cause any symptoms in its early stages, earning it the title of a “silent” disease.
Types of Fatty Liver Disease
There are two main types of fatty liver disease:
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): This type is not related to alcohol consumption and is commonly associated with obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome.
- Alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD): This type is caused by excessive alcohol consumption and can lead to more severe liver damage if left untreated.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of fatty liver disease is not fully understood, but certain factors can increase the risk of developing the condition:
- Obesity
- Type 2 diabetes
- Poor diet high in processed foods and sugars
- Lack of physical activity
- High cholesterol or triglyceride levels
- Rapid weight loss
Symptoms and Complications
In its early stages, fatty liver disease may not present any noticeable symptoms. However, as the condition progresses, individuals may experience:
- Fatigue or weakness
- Pain or discomfort in the upper right abdomen
- Swelling in the abdomen or legs
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Mental confusion or difficulty concentrating
If left untreated, fatty liver disease can lead to more severe complications such as liver inflammation (steatohepatitis), fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even liver failure.
Treatment and Prevention
Managing fatty liver disease involves lifestyle changes aimed at reducing fat accumulation in the liver. These may include:
- Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins
- Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise
- Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption
- Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels
- Regular monitoring and follow-up with healthcare providers
- In some cases, medications or surgical interventions may be recommended by healthcare professionals.
The Importance of Awareness
Fatty liver disease is a growing concern worldwide due to its association with obesity and metabolic disorders. Early detection through routine check-ups and adopting a healthy lifestyle can help prevent its progression to more severe stages. By understanding the risks and taking proactive measures, individuals can safeguard their liver health and overall well-being.
Understanding Fatty Liver Disease: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Prevention
- What is fatty liver disease?
- What are the causes of fatty liver disease?
- What are the symptoms of fatty liver disease?
- How is fatty liver disease diagnosed?
- What are the risk factors for developing fatty liver disease?
- Can fatty liver disease be reversed?
- Is there a specific diet recommended for managing fatty liver disease?
- Are there any complications associated with untreated fatty liver disease?
- How can fatty liver disease be prevented?
What is fatty liver disease?
Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition characterized by the accumulation of excess fat in the liver. This build-up of fat can lead to inflammation and damage to the liver cells, impacting its ability to function properly. There are two main types of fatty liver disease: non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), which is not related to alcohol consumption and often associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome, and alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD), caused by excessive alcohol intake. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and risk factors of fatty liver disease is crucial in addressing this common yet often overlooked health concern.
What are the causes of fatty liver disease?
Fatty liver disease can be caused by various factors, with the most common being obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome. Poor dietary choices high in processed foods and sugars, lack of physical activity, high cholesterol or triglyceride levels, and rapid weight loss are also known contributors to the development of fatty liver disease. Understanding these underlying causes is crucial in managing and preventing the condition, highlighting the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle and seeking medical advice for early intervention.
What are the symptoms of fatty liver disease?
Fatty liver disease can be challenging to detect in its early stages as it often presents with no noticeable symptoms. However, as the condition progresses, individuals may experience symptoms such as fatigue or weakness, pain or discomfort in the upper right abdomen, swelling in the abdomen or legs, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), and mental confusion or difficulty concentrating. It’s important to be aware of these signs and seek medical advice if you experience any of these symptoms to receive timely evaluation and appropriate management.
How is fatty liver disease diagnosed?
To diagnose fatty liver disease, healthcare providers typically begin with a thorough medical history review and physical examination. Blood tests may be conducted to assess liver function and check for elevated liver enzymes, indicating potential liver damage. Imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI scans can provide detailed images of the liver to detect fat accumulation and assess the extent of the condition. In some cases, a liver biopsy may be recommended to confirm the diagnosis and determine the severity of fatty liver disease. Early detection through these diagnostic methods is crucial for timely intervention and management of the condition.
What are the risk factors for developing fatty liver disease?
Understanding the risk factors for developing fatty liver disease is crucial in preventing its onset and progression. Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing this condition, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, poor dietary habits high in processed foods and sugars, sedentary lifestyle, elevated cholesterol or triglyceride levels, and rapid weight loss. By being aware of these risk factors and making positive lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, following a balanced diet, staying physically active, and managing underlying health conditions effectively, individuals can reduce their risk of fatty liver disease and promote overall liver health.
Can fatty liver disease be reversed?
Reversing fatty liver disease is possible, especially in its early stages. Making lifestyle changes such as adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce fat accumulation in the liver. By addressing underlying risk factors like obesity and insulin resistance, individuals can improve their liver health and potentially reverse the effects of fatty liver disease. It’s important to consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance on how to effectively manage and reverse this condition.
Is there a specific diet recommended for managing fatty liver disease?
When it comes to managing fatty liver disease, following a specific diet plays a crucial role in improving liver health. A diet recommended for individuals with fatty liver disease typically focuses on reducing fat accumulation in the liver and promoting overall well-being. This may involve consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while limiting saturated fats, sugars, and processed foods. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight through portion control and regular exercise is essential for managing the condition effectively. Consulting with a healthcare provider or a nutritionist can help tailor a diet plan that meets individual needs and supports liver health in the long run.
Are there any complications associated with untreated fatty liver disease?
Untreated fatty liver disease can lead to a range of complications that pose serious risks to one’s health. As the condition progresses, individuals may face liver inflammation (steatohepatitis), which can further advance to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even liver failure. These complications not only impact the liver’s ability to function properly but also increase the likelihood of developing more severe health issues. It is crucial to address fatty liver disease in its early stages through lifestyle changes and medical interventions to prevent the progression of these potentially life-threatening complications.
How can fatty liver disease be prevented?
Preventing fatty liver disease primarily involves adopting a healthy lifestyle and making mindful choices regarding diet and physical activity. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help reduce the accumulation of fat in the liver. Regular exercise plays a crucial role in managing weight and improving overall metabolic health. Limiting alcohol consumption is essential, as excessive drinking can contribute to the development of alcoholic fatty liver disease. Monitoring blood sugar levels and cholesterol, along with routine check-ups with healthcare providers, can aid in early detection and intervention if needed. By prioritizing these preventive measures, individuals can take proactive steps towards safeguarding their liver health and reducing the risk of fatty liver disease.
The Silent Threat: Understanding Fatty Liver Disease Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition that occurs when fat accumulates in the liver. While it’s normal to have some fat in the liver, excessive fat can lead to serious health issues. This condition often goes unnoticed as it may not cause any…
Latest articles
- Balancing Act: Nurturing Your Lifestyle’s Essence for Well-being
- Unveiling the Legacy of Micah Richards: A Footballing Icon
- Unveiling the Excitement: The Mexican Open Tennis Tournament in Acapulco
- Stay In the Loop: Man Utd News Now Uncovered!
- Exploring the Depths: The Fascinating World of Marine Biology
Latest comments
Archive
- March 2026
- February 2026
- January 2026
- December 2025
- November 2025
- October 2025
- September 2025
- August 2025
- July 2025
- June 2025
- May 2025
- April 2025
- March 2025
- February 2025
- January 2025
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
