Understanding Pneumonia: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Explained
by twib
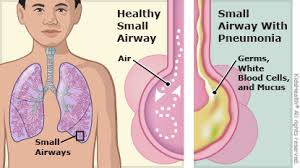
Pneumonia: Understanding the Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Pneumonia is a common yet serious respiratory infection that affects the lungs. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi, leading to inflammation in the air sacs of the lungs. This condition can range from mild to severe and can be life-threatening, especially for young children, the elderly, and individuals with weakened immune systems.
Symptoms of Pneumonia
The symptoms of pneumonia can vary depending on the cause and severity of the infection. Common signs include:
- Chest pain when breathing or coughing
- Shortness of breath
- Fever and chills
- Cough with phlegm production
- Fatigue and weakness
- Nausea or vomiting
Causes of Pneumonia
Pneumonia can be caused by various factors:
- Bacterial pneumonia: Caused by bacteria such as Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- Viral pneumonia: Caused by viruses like influenza (flu) or respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
- Fungal pneumonia: Caused by fungi found in soil or bird droppings.
- Aspiration pneumonia: Occurs when food, liquids, or vomit are inhaled into the lungs.
Treatment for Pneumonia
The treatment for pneumonia depends on the type and severity of the infection. It often includes:
- Antibiotics for bacterial pneumonia.
- Antiviral medications for viral pneumonia.
- Antifungal drugs for fungal pneumonia.
Key Benefits of Early Detection and Treatment for Pneumonia
- Pneumonia can be effectively treated with appropriate medications.
- Vaccines are available to prevent certain types of pneumonia, reducing the risk of infection.
- Early detection and treatment of pneumonia can lead to a faster recovery.
- Improved hygiene practices can help lower the chances of contracting pneumonia.
- Awareness about pneumonia symptoms can prompt timely medical intervention, preventing complications.
- Receiving proper medical care and rest can aid in the recovery process from pneumonia.
Seven Critical Drawbacks of Pneumonia: Risks, Misdiagnosis, and Complications
- Pneumonia can be life-threatening, especially in vulnerable populations.
- Symptoms of pneumonia can mimic those of other respiratory conditions, leading to misdiagnosis.
- Treatment for pneumonia may require hospitalization, impacting daily life and routines.
- Pneumonia can lead to complications such as pleurisy or lung abscess if not treated promptly.
- Recovery from pneumonia can be slow and may involve lingering fatigue and weakness.
- Certain strains of bacteria causing pneumonia are becoming resistant to antibiotics, complicating treatment.
- Individuals with chronic conditions like asthma or COPD are at higher risk of developing pneumonia.
Pneumonia can be effectively treated with appropriate medications.
Pneumonia, a respiratory infection affecting the lungs, offers a notable advantage in that it can be successfully treated with the right medications. By promptly identifying the underlying cause of pneumonia—whether bacterial, viral, or fungal—healthcare providers can prescribe appropriate antibiotics, antiviral drugs, or antifungal medications to combat the infection effectively. This targeted treatment approach plays a crucial role in helping patients recover from pneumonia and prevent complications, highlighting the importance of early diagnosis and medical intervention in managing this condition.
Vaccines are available to prevent certain types of pneumonia, reducing the risk of infection.
Vaccines are a crucial pro when it comes to pneumonia, as they offer a preventive measure against specific types of the infection. By getting vaccinated, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of contracting pneumonia caused by certain bacteria or viruses. This proactive approach not only protects the individual but also contributes to community immunity, ultimately helping to lower the overall incidence of pneumonia cases. Vaccines play a vital role in safeguarding public health and promoting well-being by providing a shield against this potentially serious respiratory illness.
Early detection and treatment of pneumonia can lead to a faster recovery.
Early detection and treatment of pneumonia play a crucial role in expediting the recovery process. By promptly identifying the symptoms and initiating appropriate medical intervention, individuals with pneumonia can experience a faster and more effective recovery. Timely treatment not only helps in alleviating the severity of the infection but also reduces the risk of complications, ultimately leading to improved outcomes and a quicker return to health.
Improved hygiene practices can help lower the chances of contracting pneumonia.
Improved hygiene practices play a crucial role in reducing the risk of contracting pneumonia. By maintaining good hygiene habits such as regular handwashing, covering coughs and sneezes, and avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick, one can significantly lower the chances of infection. Keeping living spaces clean and well-ventilated also contributes to creating a healthier environment that minimizes the spread of germs that can lead to pneumonia. Emphasizing these hygiene practices not only promotes overall well-being but also serves as a proactive measure in preventing respiratory infections like pneumonia.
Awareness about pneumonia symptoms can prompt timely medical intervention, preventing complications.
Raising awareness about pneumonia symptoms plays a crucial role in facilitating prompt medical intervention, ultimately helping to prevent potential complications. Recognizing the early signs of pneumonia, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and persistent cough, can prompt individuals to seek timely medical attention. By seeking treatment early on, patients can receive appropriate care and management that may help prevent the progression of the infection and reduce the risk of severe complications associated with pneumonia.
Receiving proper medical care and rest can aid in the recovery process from pneumonia.
Receiving proper medical care and allowing oneself ample rest are crucial factors that can significantly aid in the recovery process from pneumonia. By following the prescribed treatment plan, which may include antibiotics, antiviral medications, or other therapies depending on the type of pneumonia, individuals can help their bodies fight off the infection effectively. Resting allows the immune system to focus its energy on combating the illness, promoting a speedier recovery and reducing the risk of complications. It is essential to prioritize self-care and follow medical advice to ensure a full and successful recovery from pneumonia.
Pneumonia can be life-threatening, especially in vulnerable populations.
Pneumonia poses a significant risk of fatality, particularly among vulnerable populations such as young children, the elderly, and individuals with weakened immune systems. The severity of the infection coupled with the compromised health status of these groups can make pneumonia a life-threatening condition. It is crucial for healthcare providers to promptly diagnose and treat pneumonia in these at-risk individuals to prevent serious complications and ensure better outcomes.
Symptoms of pneumonia can mimic those of other respiratory conditions, leading to misdiagnosis.
Symptoms of pneumonia can mimic those of other respiratory conditions, such as bronchitis or the flu, which can sometimes result in misdiagnosis. The similarity in symptoms, like coughing, fever, and difficulty breathing, can make it challenging for healthcare providers to differentiate between different respiratory illnesses. This misdiagnosis may delay appropriate treatment for pneumonia, potentially putting patients at risk of complications. It underscores the importance of thorough diagnostic testing and medical evaluation to accurately identify and treat pneumonia in a timely manner.
Treatment for pneumonia may require hospitalization, impacting daily life and routines.
One significant drawback of pneumonia is that its treatment may necessitate hospitalization, disrupting daily life and routines. Being admitted to the hospital for pneumonia can be emotionally and physically challenging, as it often requires a prolonged stay away from home, family, and regular activities. The need for hospitalization can lead to feelings of isolation and dependency, affecting the individual’s overall well-being and quality of life during the recovery process.
Pneumonia can lead to complications such as pleurisy or lung abscess if not treated promptly.
Pneumonia, if left untreated, can result in serious complications such as pleurisy or lung abscess. Pleurisy is the inflammation of the lining around the lungs, causing sharp chest pain when breathing. On the other hand, a lung abscess is a collection of pus within the lung tissue, leading to symptoms like persistent coughing, fever, and difficulty breathing. Prompt treatment of pneumonia is crucial to prevent these potentially severe complications and ensure a quicker recovery for the affected individual.
Recovery from pneumonia can be slow and may involve lingering fatigue and weakness.
Recovery from pneumonia can be a gradual process, often accompanied by lingering fatigue and weakness. Even after the infection has been treated, the body may take time to fully recuperate and regain its strength. It is not uncommon for individuals recovering from pneumonia to experience ongoing tiredness and a sense of physical weakness as their immune system works to rebuild and restore their health. Patience and proper rest are essential during this period to support the body’s recovery process effectively.
Certain strains of bacteria causing pneumonia are becoming resistant to antibiotics, complicating treatment.
Certain strains of bacteria causing pneumonia are becoming increasingly resistant to antibiotics, posing a significant challenge in the treatment of this respiratory infection. Antibiotic resistance makes it harder to combat the bacterial pneumonia effectively, leading to prolonged illness, increased healthcare costs, and higher risks of complications. This growing concern highlights the importance of prudent antibiotic use, development of alternative treatment strategies, and global efforts to address antimicrobial resistance to safeguard public health.
Individuals with chronic conditions like asthma or COPD are at higher risk of developing pneumonia.
Individuals with chronic conditions such as asthma or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) face an increased risk of developing pneumonia. The compromised respiratory function associated with these conditions makes the lungs more vulnerable to infections like pneumonia. Managing these chronic illnesses effectively through proper medication and care is crucial in reducing the likelihood of pneumonia complications and improving overall respiratory health. Regular monitoring and preventive measures can help individuals with asthma or COPD lower their susceptibility to pneumonia and maintain better respiratory well-being.
Pneumonia: Understanding the Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Pneumonia: Understanding the Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Pneumonia is a common yet serious respiratory infection that affects the lungs. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi, leading to inflammation in the air sacs of the lungs. This condition can range from mild to severe and can…
Latest articles
- Balancing Act: Nurturing Your Lifestyle’s Essence for Well-being
- Unveiling the Legacy of Micah Richards: A Footballing Icon
- Unveiling the Excitement: The Mexican Open Tennis Tournament in Acapulco
- Stay In the Loop: Man Utd News Now Uncovered!
- Exploring the Depths: The Fascinating World of Marine Biology
Latest comments
Archive
- March 2026
- February 2026
- January 2026
- December 2025
- November 2025
- October 2025
- September 2025
- August 2025
- July 2025
- June 2025
- May 2025
- April 2025
- March 2025
- February 2025
- January 2025
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
