Understanding Lyme Disease: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment in Australia
by twib
Lyme Disease: An Overview
Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a bacterial infection caused by the spirochete bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi. It is primarily transmitted to humans through the bite of infected black-legged ticks.
Symptoms of Lyme Disease
The symptoms of Lyme disease can vary and often mimic other conditions, making it challenging to diagnose. Common early signs include:
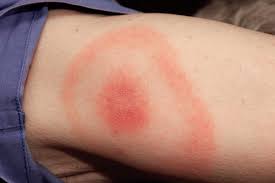
- Red rash that looks like a bull’s-eye (erythema migrans)
- Fever and chills
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Muscle and joint aches
Causes of Lyme Disease
As mentioned earlier, Lyme disease is primarily transmitted through the bite of infected ticks. Ticks become infected with the bacteria when they feed on infected animals like mice and deer. When an infected tick bites a human, the bacteria can be transmitted into the bloodstream, leading to infection.
Treatment for Lyme Disease
Early detection and treatment are crucial in managing Lyme disease. Antibiotics are commonly prescribed to eliminate the bacteria and prevent further complications. In some cases where the disease is not diagnosed early, more prolonged antibiotic treatment may be necessary.
Prevention Tips
To reduce your risk of contracting Lyme disease, consider the following preventive measures:
- Avoid areas with high tick populations like wooded or grassy areas.
- Wear long-sleeved shirts and pants when outdoors.
- Use insect repellent containing DEET.
- Perform thorough tick checks after spending time outdoors.
If you suspect you may have been exposed to ticks or are experiencing symptoms of Lyme disease, consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and treatment.
Understanding Lyme Disease: Symptoms, Transmission, Treatment, Vaccination, and Prevention
- What are the symptoms of Lyme disease?
- How is Lyme disease transmitted to humans?
- What are the treatment options for Lyme disease?
- Is there a vaccine available for Lyme disease?
- How can I prevent contracting Lyme disease?
What are the symptoms of Lyme disease?
Lyme disease presents a variety of symptoms that can differ from person to person. Commonly reported symptoms include a distinctive red rash resembling a bull’s-eye, known as erythema migrans, along with fever, chills, headaches, fatigue, and muscle or joint aches. It is essential to note that these symptoms may not always manifest in the same way for everyone, making diagnosis challenging. If you suspect you have been exposed to ticks or are experiencing any of these symptoms, seek medical advice promptly for proper evaluation and treatment.
How is Lyme disease transmitted to humans?
Lyme disease is primarily transmitted to humans through the bite of infected black-legged ticks, also known as deer ticks. These ticks become carriers of the Borrelia burgdorferi bacterium after feeding on infected animals like mice and deer. When an infected tick bites a human and stays attached for a sufficient amount of time, typically 36-48 hours, the bacteria can be transmitted into the bloodstream, leading to a Lyme disease infection. It is essential to be vigilant in areas where ticks are prevalent and take preventive measures to reduce the risk of exposure to these disease-carrying pests.
What are the treatment options for Lyme disease?
When it comes to Lyme disease, treatment options typically involve the use of antibiotics to combat the bacterial infection caused by Borrelia burgdorferi. The choice of antibiotics and duration of treatment may vary depending on the stage of the disease and individual factors. Early detection is crucial for successful treatment, as prompt administration of antibiotics can help prevent further complications. In some cases where Lyme disease is not diagnosed early, more prolonged antibiotic therapy may be necessary to effectively eradicate the bacteria and alleviate symptoms. It is essential for individuals suspected of having Lyme disease to seek medical advice from healthcare professionals for proper evaluation and tailored treatment plans.
Is there a vaccine available for Lyme disease?
In response to the frequently asked question about Lyme disease, “Is there a vaccine available for Lyme disease?” it is important to note that a vaccine called LYMErix was previously available for Lyme disease prevention. However, due to low demand and concerns about side effects, the vaccine was withdrawn from the market in 2002. Since then, research efforts have been ongoing to develop new and improved vaccines for Lyme disease prevention. As of now, there is no commercially available vaccine for Lyme disease, but researchers continue to explore potential options in the quest for effective prevention strategies against this tick-borne illness.
How can I prevent contracting Lyme disease?
To prevent contracting Lyme disease, it is important to take precautionary measures when spending time outdoors, especially in areas where ticks are prevalent. Wear long-sleeved shirts and pants to minimize skin exposure, use insect repellent containing DEET, and avoid walking through tall grass or wooded areas where ticks may be present. After outdoor activities, conduct thorough tick checks on yourself, your family members, and pets. Promptly removing any attached ticks can help reduce the risk of infection. Additionally, consider landscaping practices that discourage tick habitats around your home. If you suspect you have been exposed to ticks or develop symptoms of Lyme disease, seek medical advice promptly for proper evaluation and treatment.
Lyme Disease: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Lyme Disease: An Overview Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a bacterial infection caused by the spirochete bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi. It is primarily transmitted to humans through the bite of infected black-legged ticks. Symptoms of Lyme Disease The symptoms of Lyme disease can vary and often mimic…
Latest articles
- Stay In the Loop: Man Utd News Now Uncovered!
- Exploring the Depths: The Fascinating World of Marine Biology
- Decoding LDL Cholesterol: Navigating the Path to Heart Health
- The Legendary Legacy of the LA Angels: A Beacon in Baseball History
- Breaking Lakers News: Latest Updates and Developments from the Court
Latest comments
Archive
- March 2026
- February 2026
- January 2026
- December 2025
- November 2025
- October 2025
- September 2025
- August 2025
- July 2025
- June 2025
- May 2025
- April 2025
- March 2025
- February 2025
- January 2025
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
